
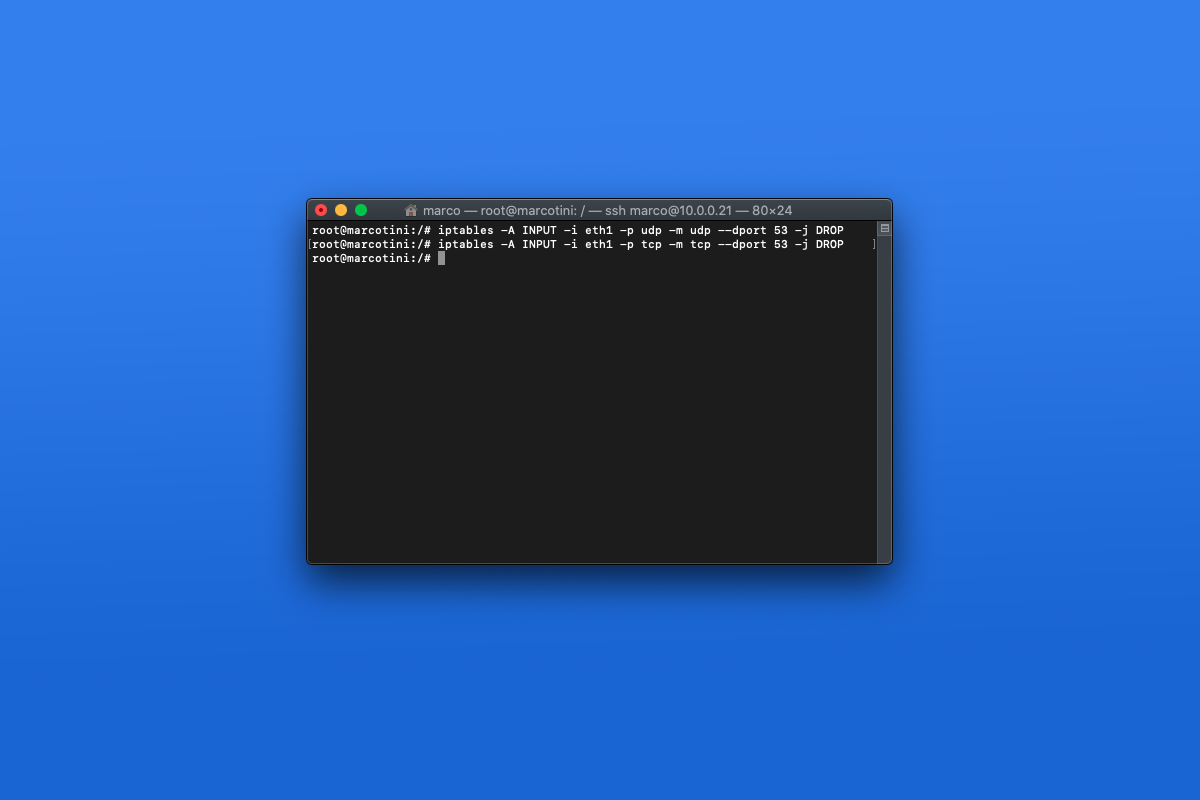
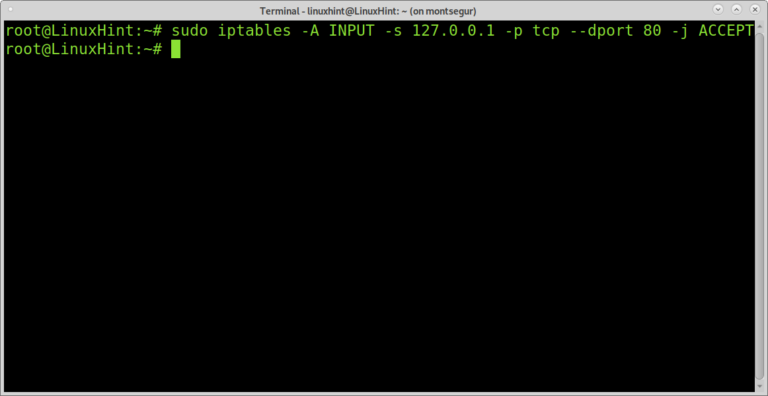
Prerouting – this chain assigns packets as soon as the server receives them.When the destination or source of the packet has to be altered, the NAT table is used. This table contains NAT (Network Address Translation) rules for routing packets to networks that cannot be accessed directly. Forward – this set of rules controls the packets that are routed through the server.Output – this chain controls the packets for outbound traffic.Input – the rules in this chain control the packets received by the server.It acts as a bouncer, deciding who gets in and out of your network. The Filter table is the most frequently used one. We will list all four along with the chains each table contains. Linux firewall iptables has four default tables. Typically, this is to accept it, drop it, or reject it (which sends an error back to the sender). Targets: A target is a decision of what to do with a packet.The outcome, where a packet is sent, is called a target. Rules can block one type of packet, or forward another type of packet. Rules: A rule is a statement that tells the system what to do with a packet.When a packet is received, iptables finds the appropriate table, then runs it through the chain of rules until it finds a match. Tables: Tables are files that join similar actions.Iptables identifies the packets received and then uses a set of rules to decide what to do with them. Data is broken up into smaller pieces (called packets), sent over a network, then put back together. Access to a terminal window/command line (Ctrl-Alt-T, Ctrl-Alt-F2).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
